AACR POSTER – p53 Hard Target
Dissecting the Biology of Mutant p53 with CETSA®
Unlocking the Complex Biology of Mutant p53 with CETSA®: Revealing Target Engagement and Stability Profiles
The tumor suppressor p53 is one of the most crucial proteins in preventing cancer, but its mutations often render it dysfunctional and a major challenge in drug development. Our study uses CETSA (Cellular Thermal Shift Assay) to investigate the binding and modulation of wild-type (WT) and mutant p53 across different breast cancer cell lines. By studying how these mutations alter p53’s thermal stability, we gain valuable insights into how tool compounds affect p53’s stability and function.
Our work demonstrates how CETSA can be applied to dissect the distinct thermal stability profiles of both WT and mutant p53 in a cellular context, revealing key differences that could inform drug discovery efforts. The study highlights the importance of using CETSA for monitoring target engagement and understanding how small molecules can modulate the activity of p53, especially in mutated forms that often escape conventional therapeutic strategies. The results show that while mutant p53 displays altered stability, these changes can be further manipulated with targeted compounds like NSC319726, presenting new opportunities for cancer therapy.
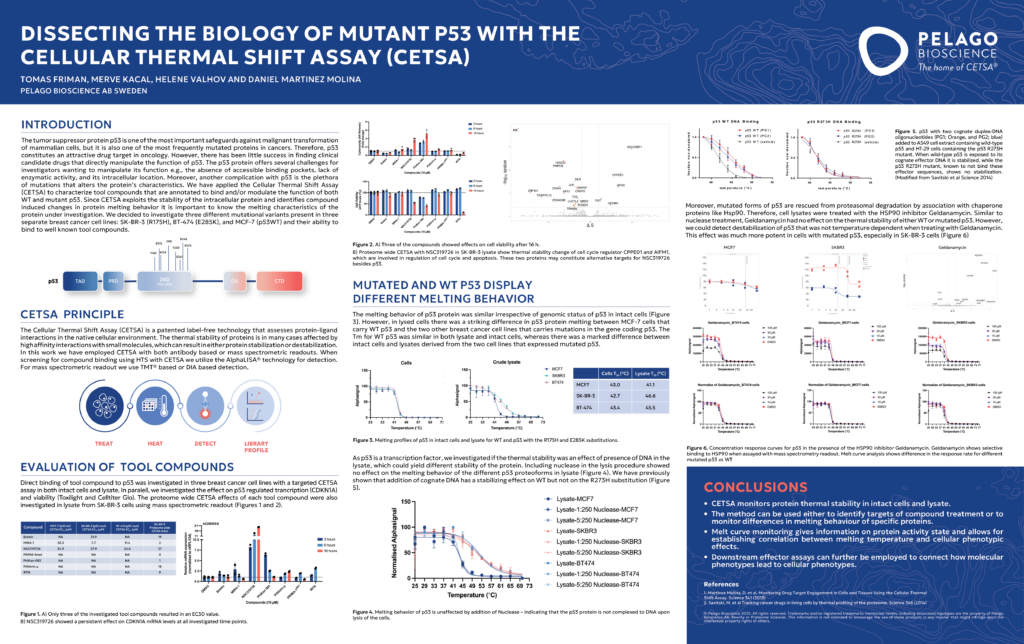
Explore how CETSA is helping to unlock the complex biology of mutant p53, paving the way for novel approaches in drug development and therapeutic targeting.
You might also be interested in
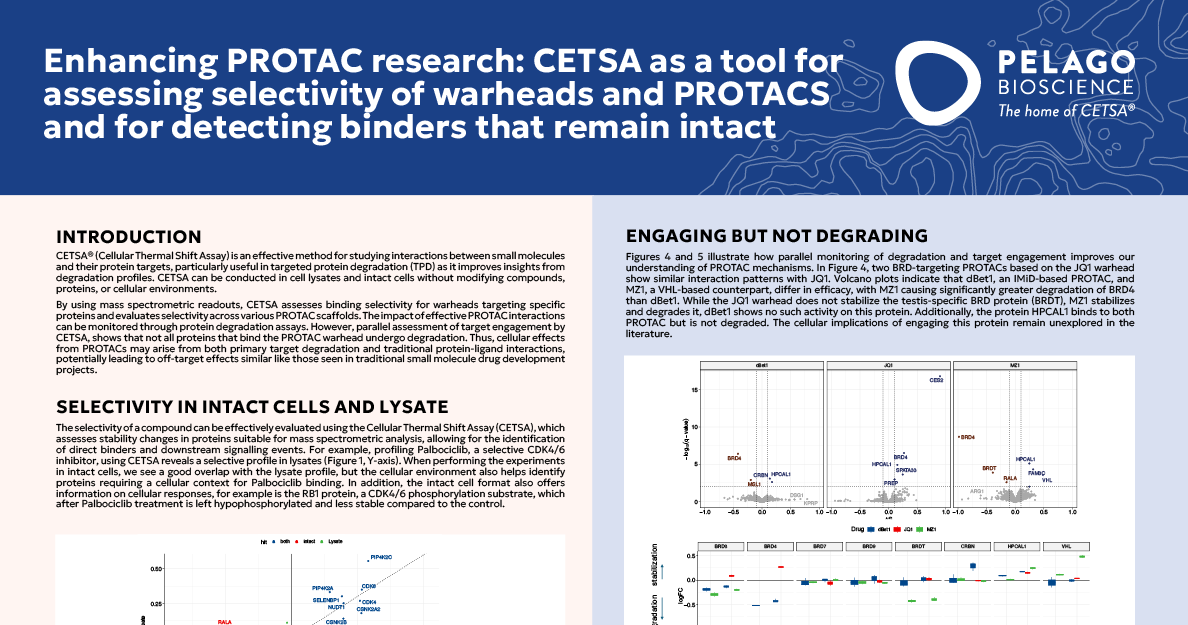
CETSA as a tool for assessing selectivity of warheads and PROTACS and for detecting binders that remain intact
CETSA® (Cellular Thermal Shift Assay) is an effective method for studying interactions between …

CETSA: Your Key to Biological Relevance
Unlock Deeper Insights in Drug Discovery with CETSA Discover how to accelerate your drug …
Are Your Degraders Delivering?
Uncover Mechanisms with CETSA® This application note explores how CETSA reveals target sp…

