AACR POSTER – p53 screening
Employing CETSA® in Primary Screening for p53 Binders
Revolutionizing p53 Binder Screening: Uncovering Potential Cancer Therapeutics with CETSA
Targeting p53, a protein often considered “undruggable” in cancer research, remains a challenging but essential task in developing novel cancer therapies. Our study utilizes CETSA (Cellular Thermal Shift Assay) to screen for p53 binders in intact SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells. This approach not only identifies compounds that bind to p53 but also reveals those that stabilize its activity, offering new opportunities for cancer treatment. By focusing on compounds active in live cells, CETSA improves upon traditional high-throughput screening (HTS) methods, which often fail to reflect true cellular biology.
This innovative method allows for rapid hit generation, efficiently identifying potential lead compounds that affect p53 functionality. Moreover, our research highlights the advantage of CETSA in providing orthogonal data to confirm target engagement and its effect on p53, ensuring a more accurate understanding of compound activity. With CETSA’s robust profiling capabilities, we enable researchers to streamline the early stages of drug discovery, prioritizing compounds with the highest potential for success in clinical development.
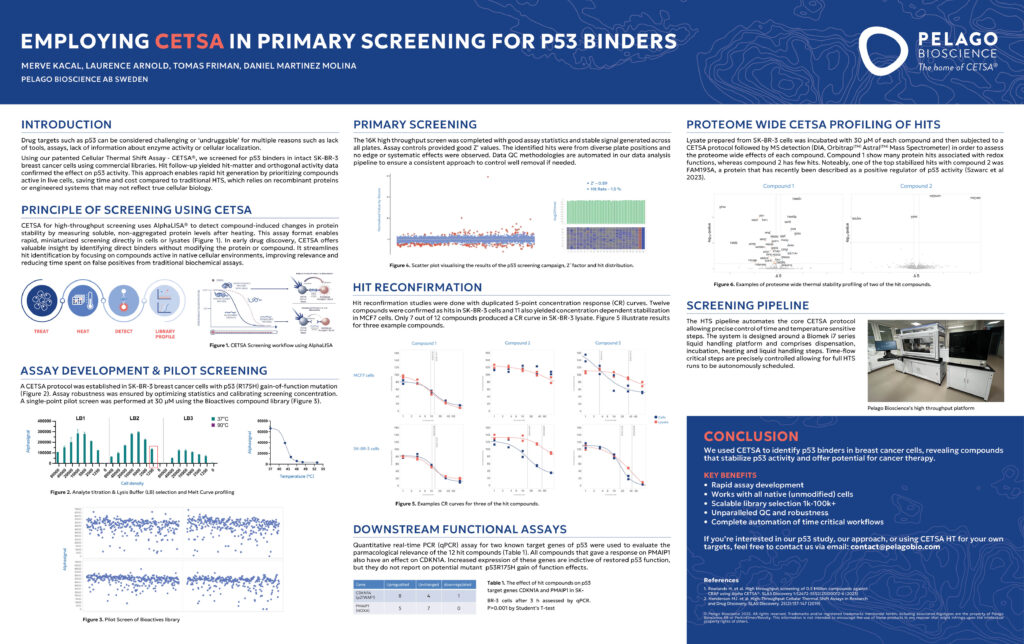
Explore how our CETSA-based screening can accelerate the identification of promising p53-targeting compounds and revolutionize cancer drug discovery.
You might also be interested in
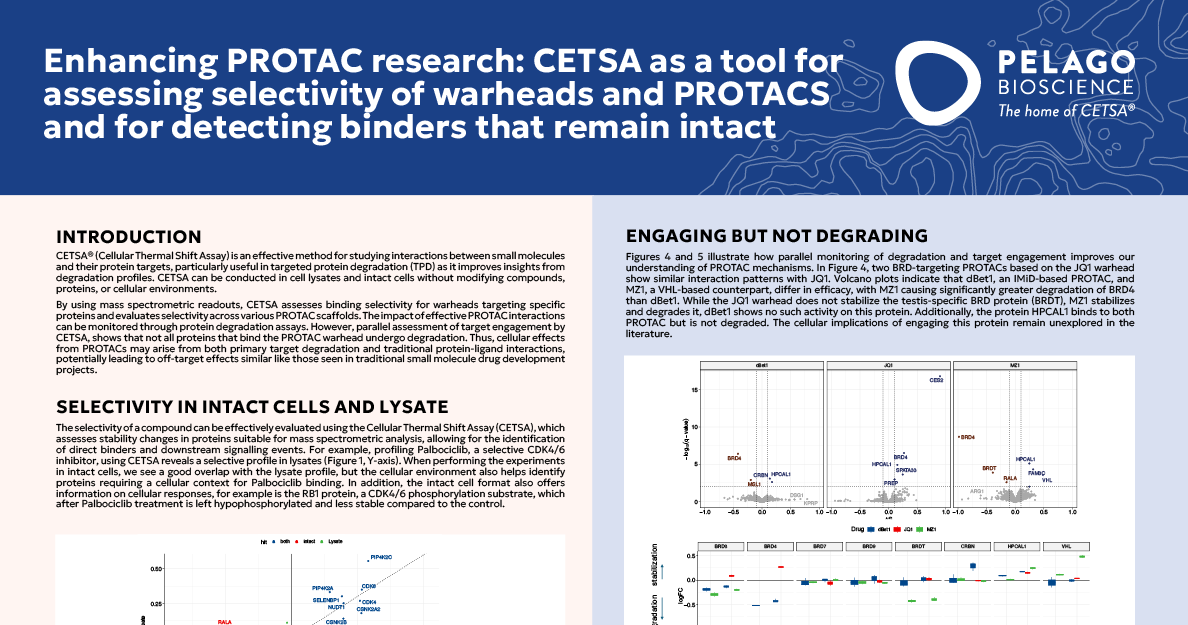
CETSA as a tool for assessing selectivity of warheads and PROTACS and for detecting binders that remain intact
CETSA® (Cellular Thermal Shift Assay) is an effective method for studying interactions between …

Enhancing Primary Screening with CETSA: A Case Study in CDK4 Hit Identification
Whether exploring challenging targets or optimizing your screening approach, this poster illust…
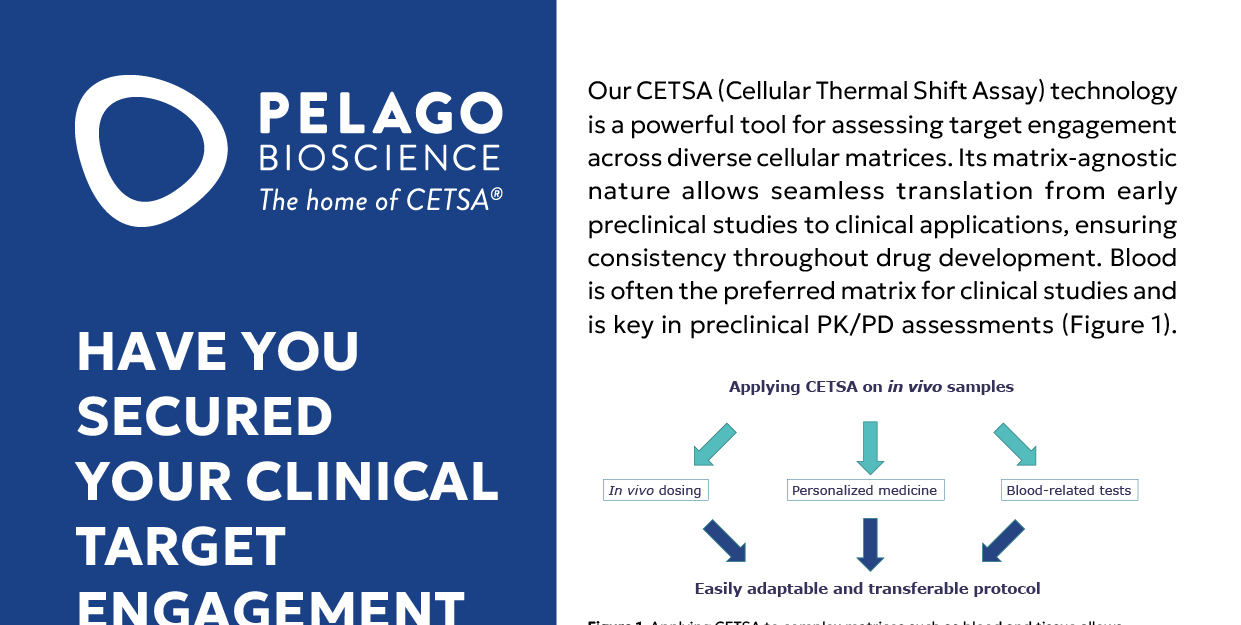
Have you Secured your Clinical Target Engagement Assay?
Harness CETSA® for Target Engagement in Whole Blood Validate target engagement with CETSA to li…

